Average Annual New Car Price Trends
Historical Trends of Average New Car Prices
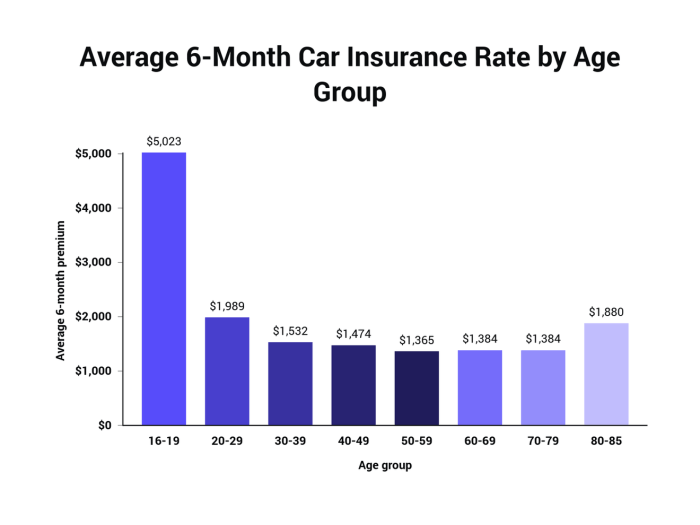
Source: spendmenot.com
Average annual new car price – The average price of a new car in the US has experienced significant fluctuations over the past few decades, influenced by a complex interplay of economic and market forces. Analyzing these trends provides valuable insights into consumer behavior and the automotive industry’s dynamics.
Average Annual New Car Prices (1980-2023)
A line graph depicting the average annual new car price from 1980 to 2023 would show a generally upward trend, with periods of steeper increases and gentler slopes. Data points would illustrate the year-over-year changes, revealing significant jumps during periods of economic expansion and relative stability during recessions. For example, a notable surge would be observed post-2020, correlating with supply chain disruptions and increased material costs.
Conversely, periods like the early 1990s might show a more moderate increase or even slight dips reflecting economic downturns.
Economic Factors Influencing Price Changes
Several key economic factors have significantly impacted new car prices. Inflation, interest rates, and fuel prices are major contributors. High inflation directly increases manufacturing and transportation costs, leading to higher sticker prices. Similarly, increased interest rates make financing more expensive, indirectly impacting demand and thus, pricing. Periods of high fuel prices often favor fuel-efficient vehicles, potentially influencing the average price depending on the market share of different vehicle types.
Price Changes Across Vehicle Classes
The average price changes haven’t been uniform across all vehicle classes. While SUVs and trucks have generally seen larger price increases over the years, driven by consumer preference and larger profit margins for manufacturers, sedans have experienced more moderate price increases or even slight decreases in some periods, reflecting shifting consumer demand.
Factors Influencing Average New Car Prices
Currently, several factors significantly influence the average new car price. Understanding these factors is crucial for both consumers and industry analysts.
Significant Factors Impacting Average New Car Prices
Three key factors currently driving up new car prices are: (1) Increased material costs (semiconductors, steel, aluminum); (2) Persistent supply chain disruptions; and (3) Strong consumer demand exceeding supply. Data from industry reports consistently show increases in the cost of raw materials and significant delays in manufacturing and shipping, directly translating into higher prices. The robust demand, particularly for certain vehicle types, further exacerbates the situation.
Inflation and Interest Rates’ Influence
Inflation erodes purchasing power, making new cars less affordable. Simultaneously, higher interest rates increase the cost of financing, further impacting affordability. This combination creates a double whammy for potential car buyers, leading to decreased demand or a shift towards used vehicles or leasing.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions and Material Costs
The ongoing impact of supply chain disruptions and escalating material costs have significantly impacted the availability and price of new vehicles. The shortage of essential components, such as microchips, has constrained production, driving up prices due to limited supply and increased demand.
Economic Factors Impact on Car Prices (Last Decade)
| Factor | Year | Impact (Percentage Change) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflation | 2014-2023 | +X% (average) | Increased manufacturing and transportation costs. |
| Interest Rates | 2014-2023 | +Y% (average increase in financing costs) | Higher borrowing costs for consumers. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | 2020-2023 | +Z% (significant increase) | Component shortages, production delays. |
| Material Costs | 2020-2023 | +W% (significant increase) | Increased prices of steel, aluminum, microchips, etc. |
Average New Car Prices Across Different Regions
Geographic location plays a role in determining the average new car price. Regional variations reflect differences in market dynamics, consumer preferences, and local economic conditions.
Regional Price Comparisons (Northeast, South, West)
Comparing the average new car prices across the Northeast, South, and West regions of the US reveals noticeable discrepancies. For instance, the Northeast might show higher average prices due to factors such as higher state taxes, higher density of population and potentially higher demand, and higher cost of living. The South, conversely, might have lower average prices due to lower overall cost of living and potentially lower demand in some areas.
The West could exhibit a mix of higher and lower prices depending on specific states and metropolitan areas, reflecting local market conditions.
Average Price Differences (Last Five Years)
A bar chart visualizing the average price differences across these three regions over the past five years would clearly show the variations. The chart’s y-axis would represent the average price, and the x-axis would represent the regions. The bars’ heights would visually demonstrate the price differences between regions for each year, highlighting the relative trends and fluctuations.
The average annual new car price fluctuates based on various market factors. Understanding past trends can help predict future costs; for instance, examining the prices from a specific year provides valuable insight. A helpful resource for researching this is the data available on 2018 new model car prices at 2018 new model car price , which contributes to a broader understanding of average annual new car price changes over time.
Reasons for Regional Price Discrepancies, Average annual new car price
Several factors contribute to these regional price differences. These include differences in state and local taxes, variations in consumer demand and purchasing power, the cost of living and transportation costs within a region, and the prevalence of different vehicle types favored in specific regions.
Average New Car Prices and Consumer Behavior: Average Annual New Car Price
The relationship between average new car prices and consumer purchasing habits is demonstrably strong. Rising prices significantly impact consumer demand and purchasing decisions.
Correlation Between Prices and Purchasing Habits

Source: mktw.net
Data on new car sales and average prices reveal an inverse relationship: as prices increase, sales often decrease. This trend is evident in historical data and current market observations. High prices lead to decreased affordability, causing consumers to postpone purchases, opt for used cars, or choose alternative purchasing options.
Impact of Rising Prices on Consumer Demand
Rising prices directly affect consumer demand. Higher prices reduce the number of potential buyers, particularly those with budget constraints. This can lead to a slowdown in new car sales and a shift towards used car markets or leasing options.
Alternative Purchasing Options
The rising cost of new cars has fueled the popularity of alternative purchasing options such as used cars and leasing. Used car prices have also increased, but they generally remain more affordable than new cars. Leasing allows consumers to drive newer vehicles without the large upfront cost of purchasing, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
Future Projections of Average New Car Prices
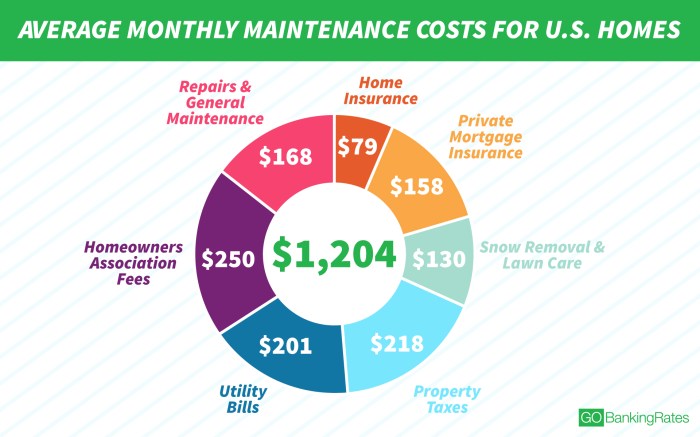
Source: gobankingrates.com
Predicting future car prices requires analyzing current market trends and anticipating future influences. Technological advancements will significantly shape the automotive landscape and pricing.
Projected Average New Car Prices (Next Five Years)
Based on current inflation rates, continued supply chain challenges (though potentially easing), and the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), a conservative prediction would suggest a continued, albeit potentially slowing, increase in average new car prices over the next five years. For instance, if the average price in 2023 is $X, we might project an increase to $Y in 2028, reflecting a gradual slowing of price increases compared to the more dramatic rises seen in recent years.
This prediction assumes a gradual stabilization of the supply chain and a continued, though possibly slower, rate of inflation.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving, will likely influence future pricing. While the initial cost of EVs is currently higher, economies of scale and technological advancements are expected to bring down prices over time. The integration of autonomous driving features may initially increase prices but could eventually lead to cost reductions through increased efficiency and safety improvements.
Projected Price Changes (Next Five Years)
| Year | Predicted Average Price | Supporting Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $Y1 | Moderate inflation, continued supply chain adjustments. |
| 2025 | $Y2 | Gradual easing of supply chain issues, increased EV production. |
| 2026 | $Y3 | Further EV market penetration, potential cost reductions in battery technology. |
| 2027 | $Y4 | Increased competition in the EV market, continued technological advancements. |
| 2028 | $Y5 | Maturation of EV technology, potential cost reductions in manufacturing and materials. |
FAQs
What are the typical financing options for new car purchases?
Typical financing options include loans from banks or credit unions, financing through dealerships, and leasing agreements.
How do government regulations affect new car prices?
Government regulations, such as fuel efficiency standards and safety requirements, can impact manufacturing costs and subsequently influence new car prices.
How do used car prices relate to new car prices?
Used car prices often follow trends in new car prices, although with a time lag. Increased new car prices generally lead to higher used car prices.
What is the impact of trade-in value on the final price of a new car?
A higher trade-in value can reduce the net cost of a new car, making it more affordable for the buyer.





















